Multiple quantile regression with XGBoost
XGBoost으로 Multiple Quantiles 을 추정하며 crossing problem을 방지하는 방법
TL;DR
이번 글에서는 XGBoost에도 Monotone quantile regressor를 만드는 과정을 소개한다. 엄청나게 LightGBM에 적용한 방식과 유사하지만.. 고로, 자세한 설명은 LightGBM 글를 봐주시면 되겠다. 코드는 RektPunk/quantile-tree에 작성해두었다.
How?
여러 작업에 치여살던 중 갑자기 잠들기전에 생각이 났다. LightGBM에서도 가능하면, 비슷한 tree 모델인 XGBoost에서도 quantile regression이 가능하지 않을까? 졸린 눈을 한 채로 검색해보니 오? 비슷하게 monotone_constraints 라는게 존재하고 tuple로 처리한다는 점만 다르다. 심지어 Custom objective function도 grad, hess를 반환하도록 구성하면 된다는 것도 확인했다. 또 dataset을 xgb.DMatrix로 쓰면 된다는 사소한 차이점까지 확인했다. 결론은 이전 LightGBM 글에서 아주 살짝만 바꾸면 끝날거 같아서 시작했다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
# module/model.py
class MonotonicQuantileRegressor:
"""
Monotone quantile regressor which preserving monotonicity among quantiles
Attributes
----------
x: Union[pd.DataFrame, pd.Series, np.ndarray]
y: Union[pd.Series, np.ndarray]
alphas: Union[List[float], float]
Methods
-------
train
predict
"""
def __init__(
self,
x: Union[pd.DataFrame, pd.Series, np.ndarray],
y: Union[pd.Series, np.ndarray],
alphas: Union[List[float], float],
):
alphas = _alpha_validate(alphas)
self.x_train, self.y_train = _prepare_train(x, y, alphas)
self.dataset = xgb.DMatrix(data=self.x_train, label=self.y_train)
self.obj = partial(check_loss_grad_hess, alphas=alphas)
def train(self, params: Dict[str, Any]) -> xgb.Booster:
"""
Train regressor and return model
Args:
params (Dict[str, Any]): params of xgb
Returns:
xgb.Booster:
"""
self._params = params.copy()
if "monotone_constraints" in self._params:
_monotone_constraints = self._params["monotone_constraints"]
_monotone_constraints.append(1)
self._params["monotone_constraints"] = tuple(_monotone_constraints)
else:
self._params.update(
{
"monotone_constraints": tuple(
[1 if "_tau" == col else 0 for col in self.x_train.columns]
)
}
)
self.model = xgb.train(
dtrain=self.dataset,
verbose_eval=False,
params=self._params,
obj=self.obj,
)
return self.model
def predict(
self,
x: Union[pd.DataFrame, pd.Series, np.ndarray],
alphas: Union[List[float], float],
) -> np.ndarray:
"""
Predict x with alphas
Args:
x (Union[pd.DataFrame, pd.Series, np.ndarray])
alphas (Union[List[float], float])
Returns:
np.ndarray
"""
alphas = _alpha_validate(alphas)
_x = _prepare_x(x, alphas)
_x = xgb.DMatrix(_x)
_pred = self.model.predict(_x)
_pred = _pred.reshape(len(alphas), len(x))
return _pred
바뀐 부분은 단순하게 DMatrix로 데이터 변형해주고, monotone_constraints를 tuple로 변경해준 것 밖에..? 마침 DMatrix도 get_label() 사용할 수 있길래 옳다구나 하고 슈슉 만들었다.
Experiment
자, 이제 동작만 테스트 해보자.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
import numpy as np
import plotly.graph_objects as go
from module.model import MonotonicQuantileRegressor
if __name__ == "__main__":
sample_size = 500
alphas = [0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7]
params = {
"learning_rate": 0.65,
"max_depth": 10,
}
x = np.linspace(-10, 10, sample_size)
y = np.sin(x) + np.random.uniform(-0.4, 0.4, sample_size)
x_test = np.linspace(-10, 10, sample_size)
y_test = np.sin(x_test) + np.random.uniform(-0.4, 0.4, sample_size)
monotonic_quantile_regressor = MonotonicQuantileRegressor(
x=x, y=y_test, alphas=alphas
)
model = monotonic_quantile_regressor.train(params=params)
preds = monotonic_quantile_regressor.predict(x=x_test, alphas=alphas)
fig = go.Figure(
go.Scatter(
x=x_test,
y=y_test,
mode="markers",
)
)
for _pred in preds:
fig.add_trace(go.Scatter(x=x_test, y=_pred, mode="lines"))
fig.show()
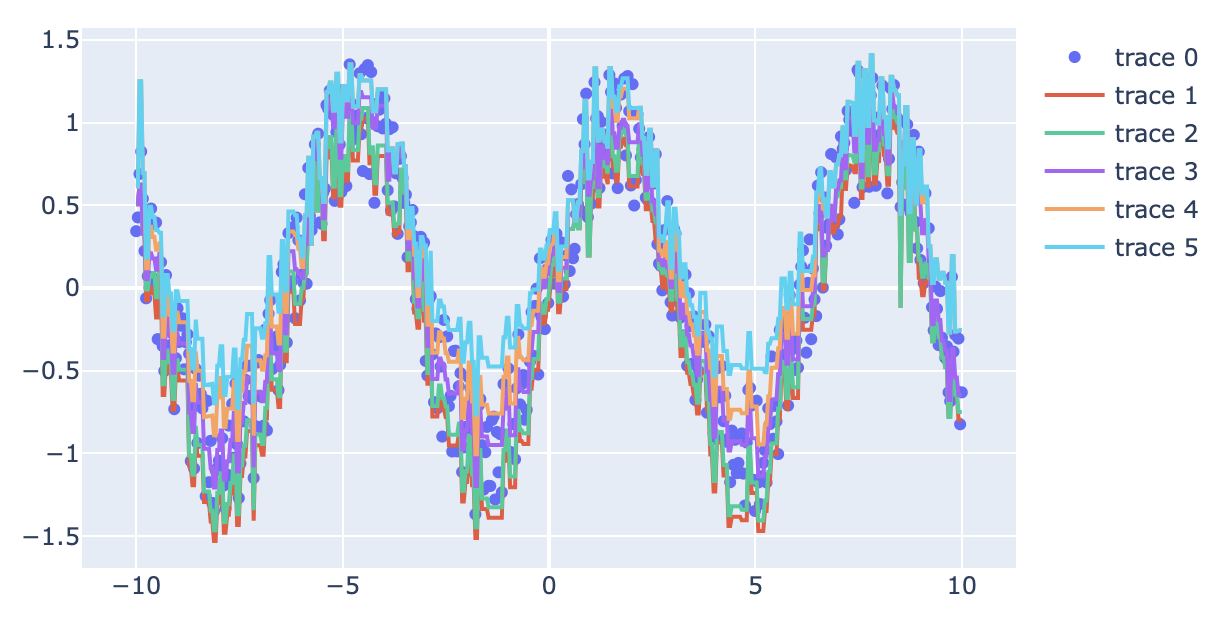 생각했던 것보다 잘 동작해서 너무 놀랐다.
생각했던 것보다 잘 동작해서 너무 놀랐다. 이게 왜 돼? 물론 성능은 언제나 그렇듯 신경쓰지 않지만.. 작은 페이퍼로 내면 될지도?
Conclusion
여러 유저가 crossing 문제로 고통받고 있는데 Issue에는 누가 질문해도 close하길래 XGBoost discuss 페이지에 올려뒀다.